meta data for this page
LamaPLC: CJMCU-219/INA-219 breakout board/IC with I²C communication
 The CJMCU-219 is a breakout board featuring the INA219 IC, a zero-drift, bidirectional current and power monitor with an I²C interface.
The CJMCU-219 is a breakout board featuring the INA219 IC, a zero-drift, bidirectional current and power monitor with an I²C interface.
Core Technical Specifications
- Voltage Measurement: Can detect bus voltages from 0V to +26V DC.
- Current Range: Measures up to ±3.2A bidirectionally using its built-in 0.1 ohm shunt resistor.
- Supply Voltage: Operates on +3.0V to +5.5V.
- Precision: Features a 12-bit ADC with a maximum error accuracy of 1% over -40°C to +85°C.
- Interface: Uses I²C communication (standard 100kHz or high-speed 400kHz/3.4MHz) with a default address of 0x40.
Key Features
- High-Side Sensing: Unlike many sensors, it can measure current on the high side (between the power source and the load), thereby avoiding ground-reference issues.
- Multi-Function Reporting: It calculates and reports bus voltage, shunt voltage drop, current, and total power (W) directly.
- Programmability: Supports software-programmable calibration, filtering (averaging up to 128 samples), and conversion times.
- Daisy-Chaining: Supports up to 16 programmable I²C addresses, allowing multiple modules to run on the same bus.
Safety & Limitations
- Voltage Limit: The chip may be damaged if bus voltage exceeds its absolute hardware limit of 26V.
- Inductive Loads: Users should be cautious with large motors, as “flyback” voltage spikes can exceed the 26V threshold and destroy the sensor.
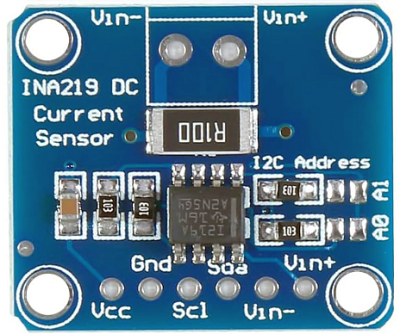
CJMCU-219 Pinout
These pins connect to your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino or Raspberry Pi) to power the sensor and transmit data.
- VCC: Supply voltage for the module (3.0V to 5.5V).
- GND: Common ground for both power and logic.
- SCL: I²C serial clock line.
- SDA: I²C serial data line.
Measurement (Load) Pins
These pins are placed in series with the positive side (high-side) of the circuit you want to monitor.
- Vin+: Connect to the positive terminal of your power source (e.g., battery).
- Vin-: Connect to the positive terminal of your load (the device being powered).
I²C addressing Pins (A0 & A1)
Some versions of the CJMCU-219 include solder pads labeled A0 and A1. By default, these are connected to GND, setting the I2C address to 0x40.
Bridging these pads to VCC allows you to set the address to any of 16 values (0x4F), enabling multiple sensors on the same I²C bus.
Caution: The maximum bus voltage the Vin pins can safely handle is 26V DC.
Arduino wiring
- VCC → Arduino 5V (o 3.3V).
- GND → Arduino GND.
- SCL → Arduino SCL (A5 on Uno/Nano).
- SDA → Arduino SDA (A4 on Uno/Nano).
- Vin+ → Positive side of your power supply.
- Vin- → Positive side of your load (the device being powered).
Arduino code
To begin using the CJMCU-219 with Arduino, the easiest approach is to use the Adafruit INA219 library.
This example code sets up the sensor and outputs voltage, current, and power readings to the Serial Monitor at 115200 baud.
A simple example with the Adafruit_INA219 library involves initializing the sensor and repeatedly reading and displaying bus voltage, shunt voltage, load voltage, current, and power. The complete code is available in the provided source document.
#include <Wire.h> #include <Adafruit_INA219.h> Adafruit_INA219 ina219; void setup(void) { Serial.begin(115200); while (!Serial) { delay(1); } // Wait for serial port to connect // Initialize the INA219 (default address 0x40) if (!ina219.begin()) { Serial.println("Failed to find INA219 chip"); while (1) { delay(10); } } // Optional: Set calibration for higher precision // Default is 32V, 2A. Alternatives: // ina219.setCalibration_32V_1A(); // ina219.setCalibration_16V_400mA(); Serial.println("Measuring voltage and current with INA219..."); } void loop(void) { float shuntvoltage = 0; float busvoltage = 0; float current_mA = 0; float loadvoltage = 0; float power_mW = 0; // Read data from sensor shuntvoltage = ina219.getShuntVoltage_mV(); busvoltage = ina219.getBusVoltage_V(); current_mA = ina219.getCurrent_mA(); power_mW = ina219.getPower_mW(); loadvoltage = busvoltage + (shuntvoltage / 1000); // Print results Serial.print("Bus Voltage: "); Serial.print(busvoltage); Serial.println(" V"); Serial.print("Shunt Voltage: "); Serial.print(shuntvoltage); Serial.println(" mV"); Serial.print("Load Voltage: "); Serial.print(loadvoltage); Serial.println(" V"); Serial.print("Current: "); Serial.print(current_mA); Serial.println(" mA"); Serial.print("Power: "); Serial.print(power_mW); Serial.println(" mW"); Serial.println(""); delay(2000); }Key Functions Explained
- begin(): Starts I2C communication. It uses address 0x40 by default.
- getBusVoltage_V(): Returns the voltage between GND and the load (V-).
- getShuntVoltage_mV(): Returns the voltage drop across the 0.1 ohm resistor.
- getCurrent_mA(): Returns the current flowing through the sensor.
- getPower_mW(): Calculates power based on the current and bus voltage.
Calibration for Accuracy
The library includes built-in calibration modes to improve precision for specific ranges:
- Default: 32V, 2A (Used if no other function is called).
- setCalibration_32V_1A(): Increases precision for current measurements up to 1A.
- setCalibration_16V_400mA(): Highest precision for low-voltage, low-current projects.
I²C topics on lamaPLC
This page has been accessed for: Today: 3, Until now: 3