meta data for this page
This is an old revision of the document!
Data block (DB)
“DB” is an abbreviation for DATA_BLOCK or the German “Datenbaustein” and is used to denote a data area. A DB can contain any set of data types allowed and defined on the given PLC. A DB can have a maximum size of 64 kByte. The size of the PLC data area limits the total space occupied by all DBs. It is important to note that the PLC is not optimized for storing large amounts of data; therefore, we do not store images, music, files, or even large text files in a DB. The TIA-Portal uses the small blue barrel symbol ( ) to denote DBs.
The image below shows the contents of a DB, along with some settings:
) to denote DBs.
The image below shows the contents of a DB, along with some settings:
The columns are as follows:
| Column | Desription |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the variable within the DB. The variable names are unique, and the DB name is displayed in the upper-left corner, in this case: K11. The variable names are supplemented with this, e.g., “K11”.liveByte. This also means that the DB can be copied and renamed one-for-one. That is, if this DB is copied and renamed to, for example, “K12”, the above reference will be “K12”.liveByte. In the case of a structure, for example, “cbUsage”, the entire structure depth must be defined, for example: “K11”.cbUsage.cbOpenClose. |
| Data type | The data type. Structures and arrays must be created when defining the DB by entering, for example, type Struct in the Data type field. |
| Offset | The offset of the variable within the DB. This appears only for non-optimized DBs. More details: optimized DB |
| Start value | The starting value of the given variables, which the PLC takes on when restarting. The default value can be overwritten in the cell. |
| Retain | Values to be retained when restarting. It can only be set for the entire DB, so it is worth grouping the values to be stored in a DB |
| Accessible from HMI/OPC UA/Web API | The value is accessible from external applications. For structures and arrays, the setting can only be defined for the entire block. OPC access can be enabled/disabled in the settings, see DB Properties. |
| Writable from HMI/OPC UA/Web API | The given value can be written from external applications. |
| Visible in HMI engineering | The setting disables or enables the HMI integration of the variable. In addition to disabling HMI, OPC can also be enabled, see DB Properties. |
| Setpoint | This allows you to initialize values in a data block (DB) online while the CPU is in RUN mode. |
| Comment | Description of the function of the field. |
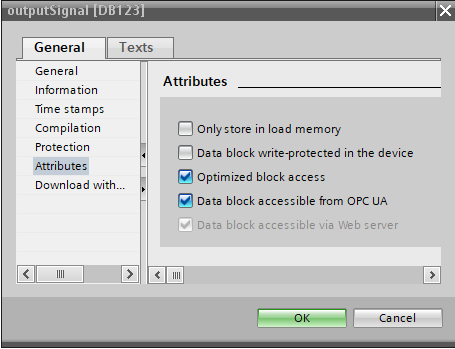
DB Properties
(right-click on the DB → Properties..)
| Name the attribut | Description |
|---|---|
| Only store in load memory | This attribute is stored on the PLC's Micro Memory Card (MMC) or similar non-volatile storage, not in the CPU's working RAM, making it ideal for large, infrequently used data such as recipes or logs. It's accessed using special instructions like READ_DBL or WRIT_DBL to transfer data to/from working memory. This preserves precious working memory, but requires explicit programming to move data for active processing. The data survives power cycles but can be lost with a factory reset. |
| Data block write-protected in the device | Make the entire data block read-only. |
| Optimized block access | Optimized variable order within the DB. See below: Optimized DB. |
| Data block accessible from OPC UA | The data block can be accessed and published by OPC UA. See: OPC UA. |
Optimized DB
Simatic groups variables in the optimized DB so they occupy as little storage space as possible. This means that it is “not visible from the outside” where a given data item is located within the storage space, i.e., in this case, the offset is not displayed in the editor window:
On the one hand, this helps better utilize the PLC's storage space. Still, on the other hand, it makes operations that require direct addressing (communication modules - Modbus, direct addressing, etc.) impossible. In such cases, this option must be disabled in the settings (right-click on the DB → Properties.. → Attributes → Optimized block access → OFF)
More information:
TIA Datatypes: S7 data types summary table